When the sun goes down, it’ll supply power to the house and eliminate the need to draw electricity from the grid.
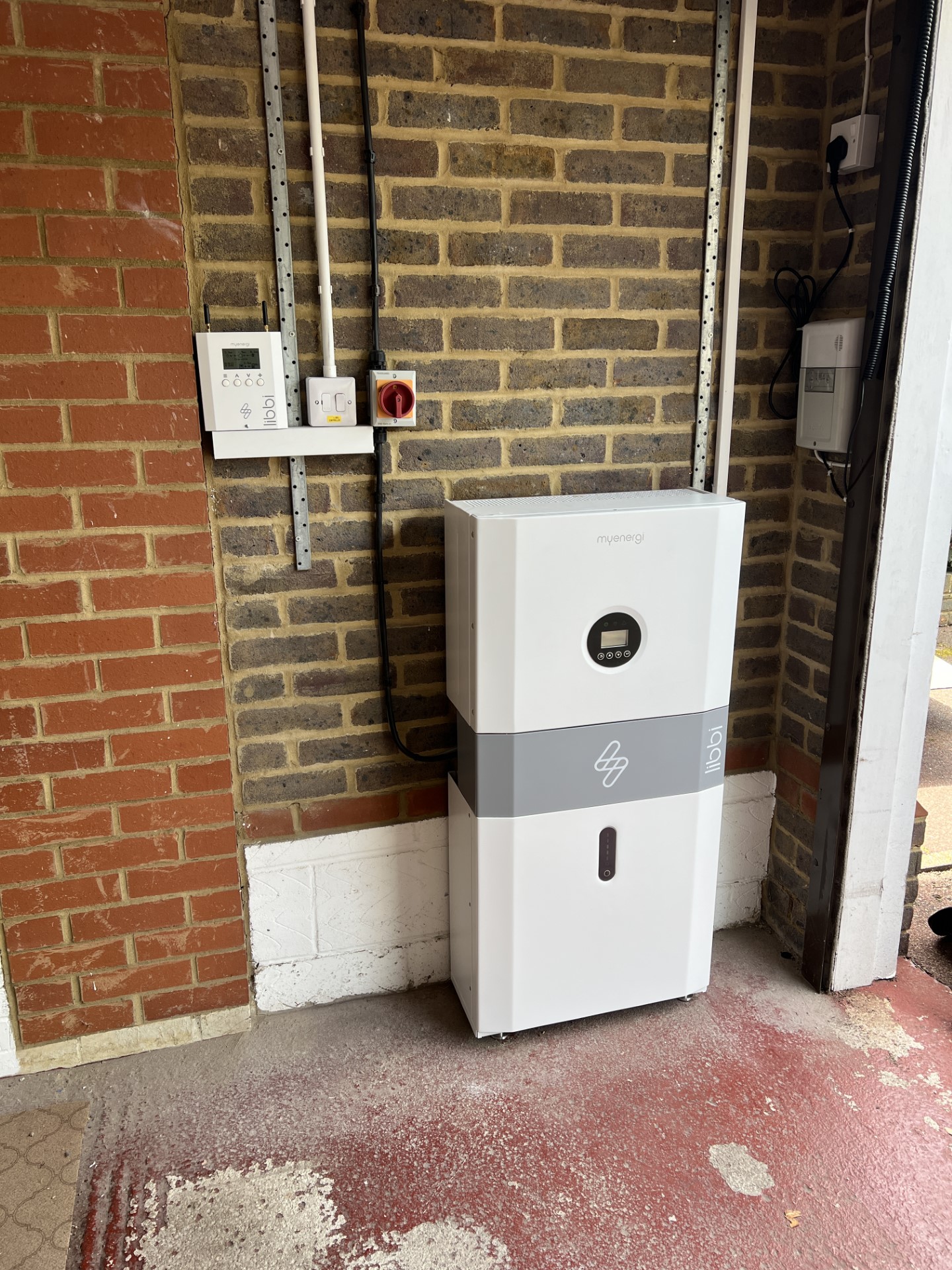
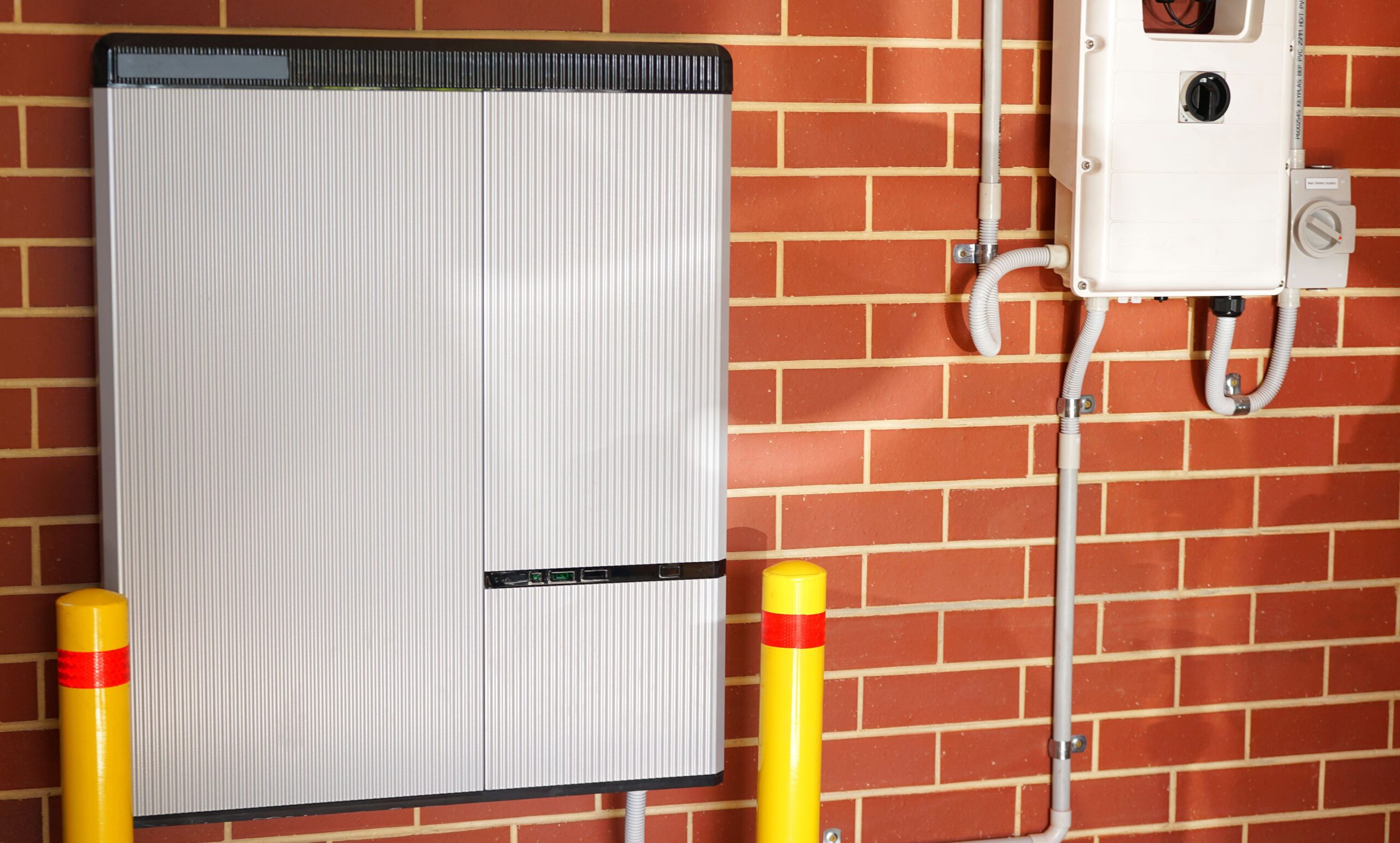


Battery storage, in the context of energy systems, refers to the use of batteries to store electrical energy for later use. There are several benefits associated with battery storage:
Load Balancing: Batteries can store excess energy during periods of low demand and release it during peak demand, helping to balance the load on the electrical grid.
Renewable Energy Integration:
Intermittency Smoothing: Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent. Battery storage helps smooth out the fluctuations in power generation, making it more reliable and consistent.
Backup Power: Battery storage systems can serve as backup power during grid outages, ensuring a continuous power supply for critical applications or in areas with unreliable grid infrastructure.
Reducing Peak Demand Charges: Businesses and utilities can use battery storage to reduce peak demand charges by drawing stored energy during periods of high demand instead of purchasing expensive electricity from the grid.
Optimising Energy Costs: Battery systems can be used to store energy during low-cost periods (e.g., at night) and discharge during high-cost periods, allowing consumers to optimise their energy expenses.
Reducing Transmission and Distribution Constraints: Batteries strategically placed in the grid can alleviate congestion in transmission and distribution systems, reducing the need for expensive infrastructure upgrades.
Clean Energy Storage: Pairing batteries with renewable energy sources contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as stored energy can be utilised when renewable generation is low.
Fast Response: Batteries can provide rapid and precise response to changes in voltage and frequency, contributing to the stability of the electrical grid.
Islanded Systems: Battery storage is crucial in remote areas or off-grid locations, providing a reliable power supply without the need for extensive transmission lines.